Overview
Heart disease is still a major global health concern, claiming millions of lives each year. Coronary angioplasty is a common treatment for coronary artery disease (CAD).
Angioplasty is performed on roughly 4.5 lakh patients in India each year. Worried about how risky coronary angioplasty is? Also, how much does angioplasty cost? Let’s find out!
What is Coronary Angioplasty? 1
Coronary angioplasty is a minimally invasive medical procedure to repair blocked coronary arteries. The coronary artery supplies blood to the heart muscle.
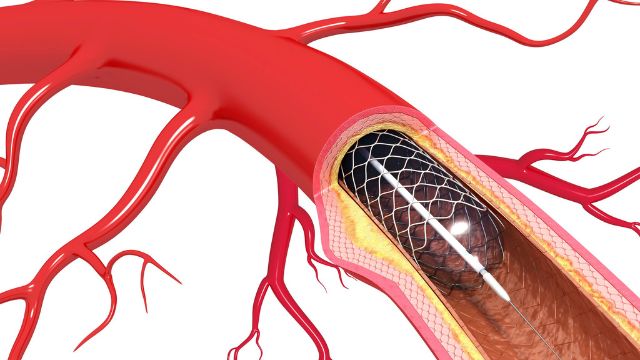
The blockage is often caused by atherosclerosis (the accumulation of cholesterol and fatty deposits). This can result in decreased blood flow, chest pain (angina), and even heart attack.
Benefits of Coronary Angioplasty 2
Coronary angioplasty has numerous advantages. They emphasise its importance in improving patients’ quality of life and lowering heart-related problems. These benefits include:
- Restores Blood Flow: The procedure improves oxygen supply and delivers nutrients to the heart by opening restricted coronary arteries. It alleviates symptoms like chest pain (angina) and increases overall heart function.
- Reduces Angina: Chest discomfort or pain caused by decreased blood flow to the heart can significantly influence a person’s quality of life. Angioplasty can effectively relieve angina symptoms. It allows people to participate in physical activities and everyday routines with less discomfort.
- Reduces the Risk of Heart Attack: Coronary angioplasty helps lower the risk of heart attacks or myocardial infarctions. The technique helps reduce the progression of unstable angina to a heart attack by quickly opening clogged arteries.
- Minimally Invasive Procedure: This treatment is simpler than standard open-heart surgery. A tiny incision is made to access the blood vessels, generally at the wrist or groyne. As a result, recovery is faster, and the risk of complications associated with major surgery is minimised.
- Stent Technology: A stent is used in various angioplasty treatments to assist in keeping the treated artery open. Stents are frequently coated with medication that slowly dissolves into the artery. It avoids restenosis (re-narrowing) and lowers the risk of subsequent blockages.
The Procedure of Coronary Angioplasty 3
Coronary angioplasty is a minimally invasive treatment. It is carried out by a heart specialist and a team of highly trained cardiovascular technicians. Here are the steps:
- Preparation: Before the surgery, the patient has to undergo a series of examinations. This includes:
- Physical examination
- Review of medical history
- Diagnostic tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram
- Stress tests
These tests assist the medical team in determining the severity and location of coronary artery blockages.
- Anaesthesia: Typically, the technique is performed in a catheterisation lab (cath lab). A local anaesthetic is used to anaesthetise the area where the catheter will be inserted. It is commonly in the groyne or wrist. In rare cases, conscious sedation may be administered to help the patient relax.
- Catheter Insertion: A catheter is a thin, flexible tube put into a blood vessel. Fluoroscopy (a type of X-ray imaging) is used to guide the catheter through the blood vessels and into the coronary arteries.
- Guidewire Insertion: A guidewire (a thin, flexible wire with a tapered tip) is put through the catheter into the blocked coronary artery. The guidewire serves as a guide for the procedure’s subsequent steps.
- Angiography: A contrast dye is administered through the catheter after inserting the guidewire. This enables clear visibility of the coronary arteries on a monitor using X-ray imaging, also known as coronary angiography.
- Balloon Inflation: A balloon catheter is a small, flexible tube with a tiny balloon at the tip. When placed into the blocked artery, this balloon collapses and inflates once it reaches the blockage caused by fatty deposits.
- Stent Placement: The artery is usually kept open with the help of a stent. The stent is a tiny metal tube that resembles mesh. It is positioned at the area of obstruction, compressed around the balloon. As the balloon is inflated, the stent swells and presses against the artery walls to keep them open.
- Balloon Deflation and Removal: The balloon is deflated and removed once the stent is securely placed. This leaves the stent in the artery to maintain blood flow.
- Final Checks and Monitoring: The catheter is removed, and pressure is put on the insertion site to stop bleeding. For a short while, the patient is closely observed to make sure that there are no complications.
- Recovery: Most patients can resume their normal activities within a day or two of the operation. But, depending on the circumstances, some patients may need to spend the night in the hospital for observation.
Is Coronary Angioplasty Safe? 4
Coronary angioplasty is typically considered safe and has developed significantly over time to become successful. Let’s look at the safety aspects of coronary angioplasty:
- Risk Evaluation: A team of healthcare professionals assesses the patient’s general health and decides whether the risks outweigh the advantages of angioplasty. Some risks are connected with coronary angioplasty. These are some examples:
- Bleeding or Haematoma: The catheter insertion site might cause bleeding or haematoma (collection of blood under the skin).
- Allergic Reactions: Some people may be allergic to the contrast dye used during the treatment.
- Blood Vessel Damage: In rare cases, blood vessels can be injured during catheter insertion.
- Arrhythmias: The surgery can cause irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) in some patients.
- Complications: While complications are rare, they may occur. These could include:
- Coronary Dissection: It occurs when the inner layers of a coronary artery detach or rip away from the outer layers.
- Clots: Some people may have clotting when a foreign object, like a stent, is in close contact with their blood.
- Restenosis: In some circumstances, the treated artery can narrow again over time (restenosis). It can occur due to vascular healing response.
- Long-Term Factors: Continuous success and safety depend on medication adherence, lifestyle modifications, and regular medical follow-up.
The safety of coronary angioplasty can vary depending on the individual’s health and specific circumstances. Before the procedure, patients should have a detailed discussion with their cardiologist to assess the risks and benefits and address any concerns.
Post-Treatment Measures 5
Post-coronary angioplasty treatment measures are essential for assuring a smooth recovery and the procedure’s success. Consider the following strategies:
- Medication Adherence: Follow your healthcare provider’s medicine instructions. This could include:
- Antiplatelet medications (such as aspirin or clopidogrel) to prevent blood clots
- Remedies for reducing cholesterol
- Blood pressure control drugs
- Lifestyle adjustments: Making healthy lifestyle adjustments can improve heart health and lower the risk of future cardiovascular events. Take a look at the following:
- Heart-Healthy Diet: Adopt a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars. This diet will support the recovery process and prevent further cardiovascular issues.
- Regular Physical Activity: As your healthcare professional directs, exercise regularly. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week to improve overall health.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a significant contributor to heart disease. Quitting smoking is one of the most helpful moves for your heart health.
- Weight Control: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight to lessen the pressure on your heart and the risk of other problems.
- Follow-up appointments: Attend all planned follow-up appointments with your cardiologist. Regular check-ups enable a doctor to monitor the progress, change medications as required, and address any concerns one may have.
- Blood Pressure and Diabetes Management: If you have diabetes or high blood pressure, consult your medical team to treat these conditions effectively. Controlling these risk factors is critical for avoiding future cardiac problems.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can harm your heart health. Deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or indulging in hobbies that you enjoy are all stress-relieving approaches.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: If you consume alcohol, do it in moderation. This is recommended to avoid elevated blood pressure levels and overall well-being.
Coronary Angioplasty Cost 6
The coronary angioplasty cost typically ranges from INR 1,20,000 to INR 2,50,000 or more. The cost differs due to certain factors, including:
- Hospital Charges
- Doctor’s Fees
- Anaesthesia and Medications
- Diagnostic Tests
- Stent Type and Cost
- Number and severity of blockage
- Hospital Stay
It is important to understand that these numbers are estimates and can vary. Additionally, certain hospitals could offer various cardiac surgery packages or financing options. By reducing out-of-pocket costs, health insurance can also assist patients in saving money.
Takeaway
Coronary angioplasty has become a cornerstone in treating CAD because it can restore blood flow and enhance heart function quickly. The procedure is safe and simple to perform.
Patients and healthcare providers must have an in-depth discussion about coronary angioplasty procedure and its cost. For further information on coronary angioplasty or any other medical concern, please contact HexaHealth. It is a HealthTech platform that will guide you and assist you in locating the best hospitals and doctors. So, make your appointment today!
References:
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coronary-angioplasty/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/heart-attack/angioplasty
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/coronary-angioplasty/about/pac-20384761
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coronary-angioplasty/risks/#:~:text=As%20with%20all%20types%20of,where%20the%20catheter%20was%20inserted, https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/coronary-angioplasty/about/pac-20384761
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/coronary-angioplasty/about/pac-20384761, https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000091.htm
- https://www.hexahealth.com/treatment/angioplasty-cost

